What men should know about Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)?
How can you prevent UTI?

Dr. Sudarshan S.
Urinary tract infections (UTI) are less common in men than in women. However, men can get UTI if they have some of the risk factors mentioned below.
Risk factors for UTI in Men:
Sexually transmitted infections. Greater incidence is seen in men who have anal intercourse.
- Diabetes Mellitus and immunocompromised conditions.
- Prostate enlargement in older men.
- Chronic indwelling urinary catheters
- Anatomical abnormality of the urinary tract.
- Cognitive impairment, urinary incontinence in elderly men.
Presentation of UTI in men:
Pain and burning sensation while passing urine. Pain may be at the penis or lower abdomen and sometimes at the back.
- Urinary urgency and frequency
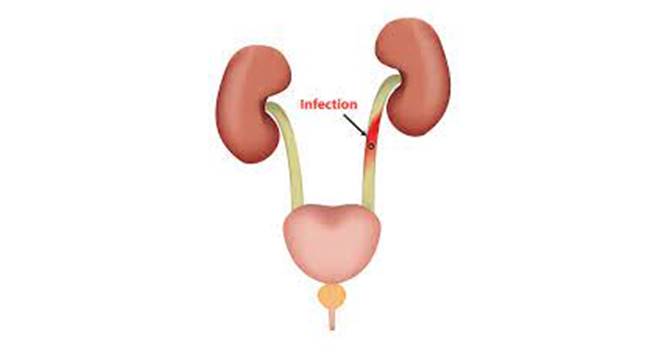
- If the infection spreads to the upper urinary tract like kidneys and ureters, one can develop fever, chills, abdominal pain, back pain, and vomiting.
- Sometimes the infection can involve the genital tract such as epididymis and testis. This presents as pain and swelling over the scrotum.
Diagnosis of UTI:
If you have symptoms suggestive of UTI, do not panic. Please consult your doctor for advice.
- The doctor will examine you clinically to confirm the diagnosis and to look for any complications.
- You may be subjected to additional tests that include urine analysis, urine culture, and sensitivity to identify the bacteria and its susceptibility to antibiotics. Sometimes imaging in the form of ultrasound or CT scan is recommended if the infection appears to be severe or complicated.
- STDs like gonorrhea and chlamydia are diagnosed clinically. The doctor may run additional tests to confirm the bacteria.
Treatment of UTI:
- Antibiotics are recommended in the treatment of UTI.
- The duration of antibiotic treatment depends on the type of UTI and severity.
- For eg., upper UTI involving kidneys usually require inpatient management and intravenous antibiotics.
- It’s equally important to monitor other parameters like hydration and temperature.
- Infections of the Prostate and urinary bladder can be managed in an outpatient setting. Prostate infection may require antibiotics for up to 4 weeks.
- Treatment of STD is specific to the organism causing it.
- Rarely, surgical intervention is required if there’s an obstruction to urinary passage or pus collection in the kidneys.
- You should follow the advice of your doctor and take medications as per prescription. Complete the course of medications and antibiotics as per the advice even if you feel better.
- Please remember that the earlier the treatment is started, the better is the outcome.
How can you prevent UTI?:
Adequate fluid intake is necessary. This helps in clearing the potentially infective organisms, from the urinary passage. During summer times, increase your water intake and stay well hydrated.
- Avoid holding urine for a long time. Empty the bladder whenever there’s an urge to urinate.
- Regular usage of condoms during sex prevents STDs.
- If you have problems related to your prostate gland, please get it checked by your doctor. Some medications ease the urinary flow.
- If you are having diabetes, the disease should be well controlled. Please follow a proper diet regimen, lifestyle changes, and take medications in time.
- Hygiene and appropriate care of urinary catheters cannot be overemphasized.
- Have regular follow-ups with your doctor if you have any underlying medical condition that might increase the risk of acquiring UTI.
Dr. Sudarshan S.
MBBS, DNB Family Medicine, Consultant Physician,
Medall Healthcare Pvt Ltd.





